The Richter Economic Timeline: What was known or knowable and what did the market say?
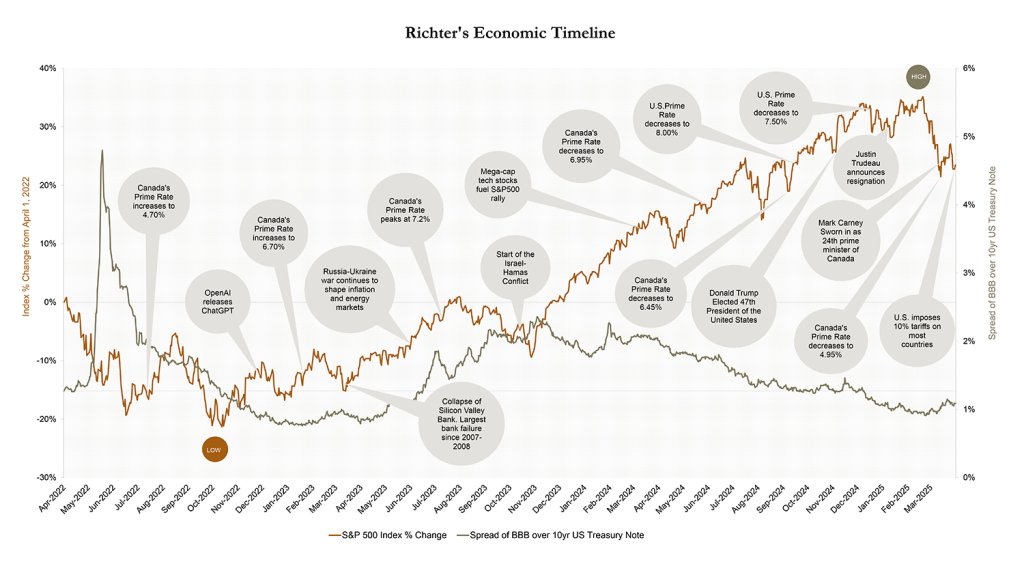
The Richter Economic Timeline
Sources: Available upon request
Richter’s economic timeline plots local and world events together with a depiction of the volatility of the stock market (S&P 500) and credit markets (the spread of publicly traded BBB corporate bonds over U.S. treasury notes).
U.S. stocks lost $6.6 trillion in Q1 2025 after the government announced larger-than-expected tariffs, sparking fears of a global trade war. Reciprocal tariffs are driving market volatility and raising costs across sectors including steel, commodities, and automobiles—costs likely to be passed on to consumers. With slowing growth and rising inflation, the U.S Federal Reserve and Bank of Canada face a difficult policy environment amid recessionary risks and upcoming the Canadian elections.
Equity markets and bond yields are likely to experience continued volatility in response to the broader macroeconomic uncertainty. This occurs contemporaneously with the following:
- The Bank of Canada and U.S. Federal Reserve have cut rates, and officials may now prioritize further rate reductions to support economic growth amid the uncertainties of a trade war.
- Unemployment rates in Canada and the U.S have slightly increased and are expected to continue rising amid ongoing trade tensions.
- Despite the AI boom of the prior quarter, innovative tech stocks (MATANA*) have collectively lost trillions of market value over the past weeks, especially those reliant on foreign production.
- Despite an initial ceasefire and hostage deal, the October 7th Israel-Hamas War has escalated into a broader regional conflict, as negotiations collapsed, and the original ceasefire expired. Contemporaneously, there are continued concerns and uncertainties over the sustained military invasion of Ukraine by Russia.
- Geopolitical and environmental disruptions have impacted global maritime trade, significantly extending shipping times. In response, international players have recently become more directly involved in addressing threats to key shipping routes.
- The new U.S. administration, backed by a Republican-controlled Senate, has emphasized lower taxes, decentralization of federal departments, and a focus on domestic energy and manufacturing production. Trade tariffs and rising fiscal deficits have prompted governments and businesses worldwide to implement countermeasures, including reciprocal tariffs, in response to these protectionist strategies.
- Canada’s housing market has slowed amid economic uncertainty and trade tensions, with affordability remaining a key challenge—particularly for first-time buyers.
- As Canada heads toward a federal election, changes in leadership, policy direction, and uncertainties on tariffs could impact fiscal spending, energy, housing, and trade.
*MATANA describes the market’s technology leaders – Microsoft, Apple, Tesla, Alphabet, Nvidia and Amazon.
This timeline was compiled by Richter Inc.’s Business Valuation and Dispute. A similar version was published in the CBV Institute’s Journal Advisory Group.
Link: https://cbvinstitute.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/CBV-Institute_Journal2020_Final.pdf

